Are you using the right search tool for your data and users?
For enterprises, search should be a powerful tool to help employees and customers quickly find answers to their questions. But with the proliferation of digital content, companies now have more data in more formats than ever before, finding useful information in that data using traditional search tools becomes impossible. Unstructured data like documents, e-mails, and pictures make up 80% of the world's information. Imagine what you can do if you could quickly unlock the valuable information within this data.
Not all search tools are created equal. A search solution must effectively process large amounts of data indifferent shapes and forms to provide accurate and relevant results.
In this blog, we'll take a closer look at four approaches to search to help shed some light on the differences of those implementations.
Using a keyword-based search tool to query structured data
Structured data has a standardized, pre-defined format typically stored in data warehouses or database systems. Traditional keyword-based search tools are effective at finding information in structured data. Users can break a question into separate (key)words when searching. The search algorithm then matches those keywords with the data living in a warehouse or other storage system and returns the matched result to the user.
One of the most popular use cases for this type of search is to find a product on an eCommerce website. For example, when a female user wants to find a pair of running shoes on Nike.com, she can type "Nike running shoes women" and receive a list of Nike brand running shoes for women in return.
Using a keyword-based search tool to query unstructured data
Unlike structured data, unstructured data such as text, images, or audio has varying shapes and forms that do not fit into a standardized format. When a user attempts to use a keyword search to find information in unstructured data, the outcome is terrible. The keyword search tool either finds no result or sends back a long list of answers covering a wide range of topics, requiring the user to spend time sifting through results to find relevant information. This is because a keyword-based search is not designed to effectively process and interpret the complexity of unstructured data. To find the correct answers in those data, a search tool must understand all the nuances in language.
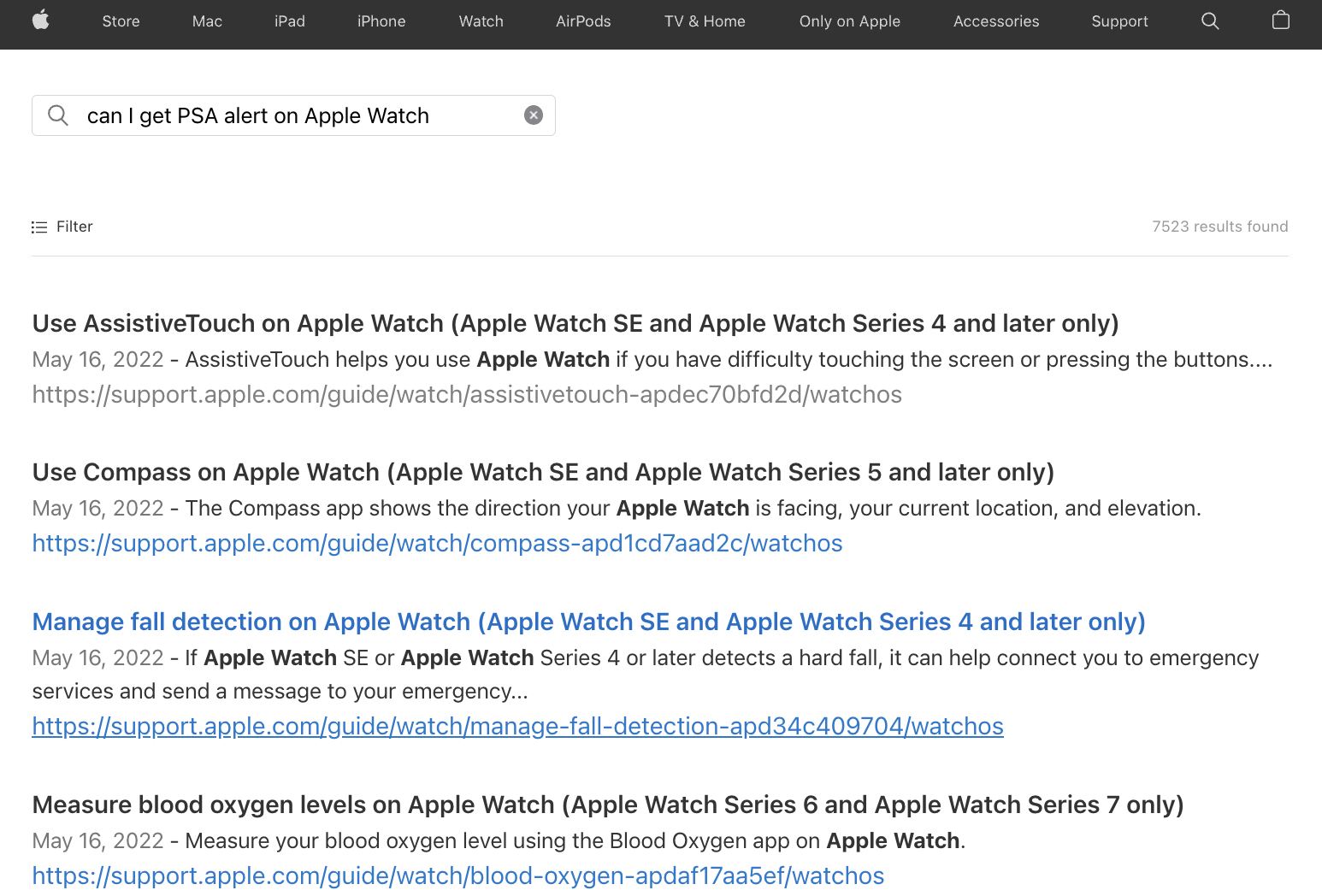
For example, suppose you want to know if you can get PSA alerts on your Apple Watch. You type "Can I get PSA alert on AppleWatch" into the search bar on Apple's support site. What you get in return is a list of answers (see below) that don't answer your specific question. You see topics about Apple Watch’s Assistivetouch feature, how to use the compass feature on Apple Watch, but nothing about receiving PSAs. It looks like the search function either didn’t understand what PSA stands for, and/or failed to interpret your question entirely, so it is not surprising that it could not retrieve the relevant information. Finding the right answers in text data to address those types of questions requires a different tool than a keyword-based solution.
Using a natural language-powered search tool to query structured data
Many organizations are now turning to advanced search solutions enabled by Natural Language Processing (NLP) technologies to empower more business users with data-driven insights. NLP is a form of artificial intelligence that allows computers to process and interpret human language effectively. An NLP-enabled search tool allows a business user to ask an analytics question in their own words through a search interface. The search returns highly accurate insights in the form of a Business Intelligence (BI) dashboard or report back to the user. Those NLP-powered search tools have sophisticatedNatural Language Understanding (NLU) capabilities, so they intuitively understand words and all the intricacies in human language. That deep understanding allows business users to ask questions using their own vocabulary, as if they were asking a knowledgeable person, and get accurate analytics insights any time they want. Business users no longer have to learn keywords, syntax, programming skills, or relying on IT for answers. Those advanced tools make data and analytics accessible to business users, empowering everyone to make informed decisions.
For example, if a sales leader wants to know the week-by-week sales trend for a particular product. He can type the question"How are this week's sales compared to last week's for Nike running shoes for Women?" into the search interface of an NLP-based search tool and receive up-to-date, accurate sales dashboards and charts instantly.
Using a natural language search tool to query unstructured data
We already knew that a keyword-based search is inferior when using it to find answers in unstructured data such as free-form text documents. To do this right, you need an intelligent search solution that can effectively process and interpret unstructured data. Using a smart search means that the tool must be capable of understanding the question and the unstructured text content. This use case is where natural language solutions like Kyndi Natural Language Search come into play.Kyndi's Natural Language Search employs sophisticated NLP techniques such as lemmatization, lexicon, and intent detection for the search algorithm to obtain a deep understanding of the question and to retrieve the most relevant and context-aware information from the underlying data.
As we saw in the Apple support example, when searching unstructured text data, you can get far better search results with an NLP-powered search. Let's ask the same question, "CanI receive PSAs on my Apple Watch?" using Kyndi Natural Language Search. Right off the bat, Kyndi returns a list of relevant answers you can use immediately. Since the results are organized by the relevance score, the most accurate answers are always presented at the top of the list, saving you from sifting through the entire page.
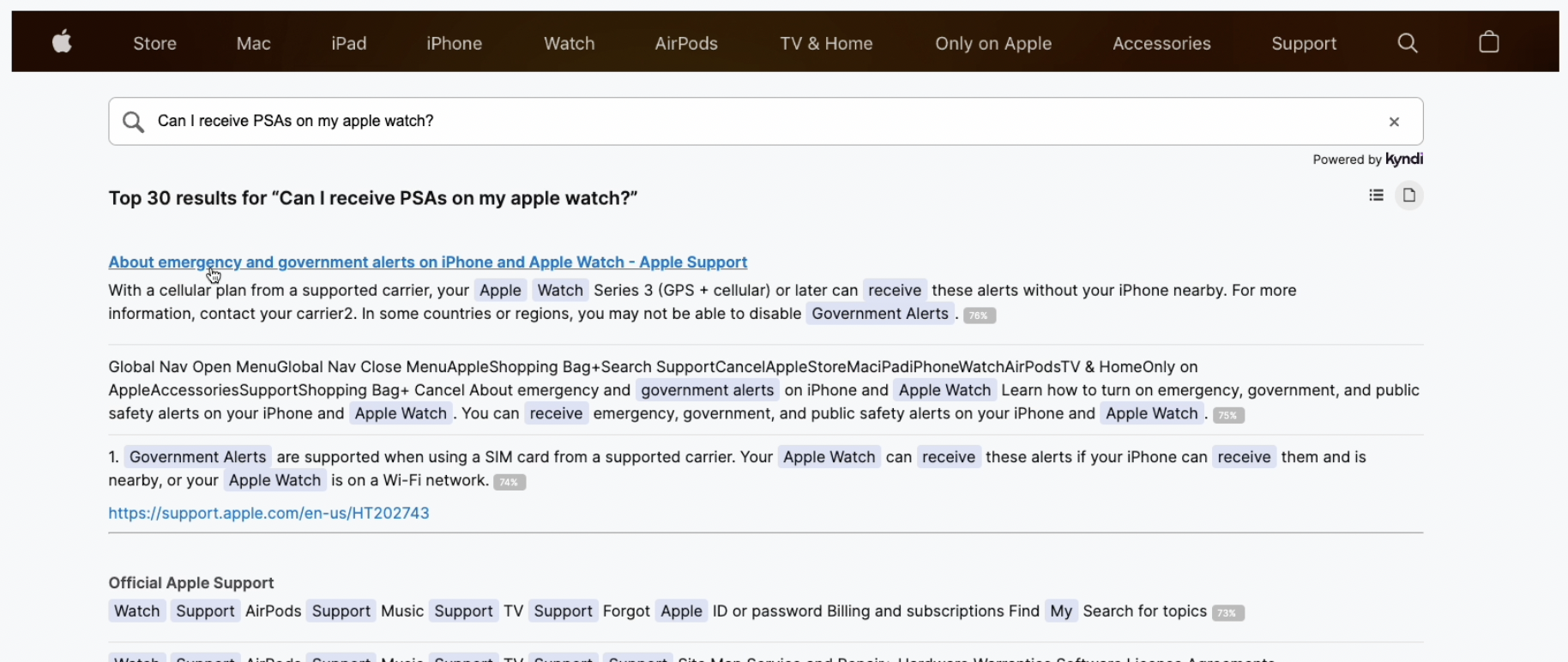
A natural language-powered search solution delivers a far superior search experience than a keyword-based alternative if you want to find the correct answers in unstructured data such as text. Like the Apple Support search example we shared, companies can leverageNLP-enabled search to help customers and employees quickly find answers in support documents across various content repositories, thereby driving better customer and employee experience.
Summary
The old saying "Use the right tool for the job" applies to search, too. When selecting a search solution, you need to consider two important factors: 1. the type of underlying data you want to search against; and 2. the user persona you wish to serve. With that in mind, choosing the right tool to get the best results is much easier.
Curious about Kyndi NaturalLanguage Search and how it can help you? Reach out, and our NLP experts are happy to give you a live demo anytime.



.png)

